React Native를 위해 알아야할 기본적인 ES6문법
간단한 문법만 연습해 볼 것이기 때문에, VS code를 이용하여 진행
먼저 vscode에 js파일을 돌릴 수 있도록 개발환경을 구축해야한다.
VScode를 이용해서 .js 개발환경을 구축
1. code runner설치
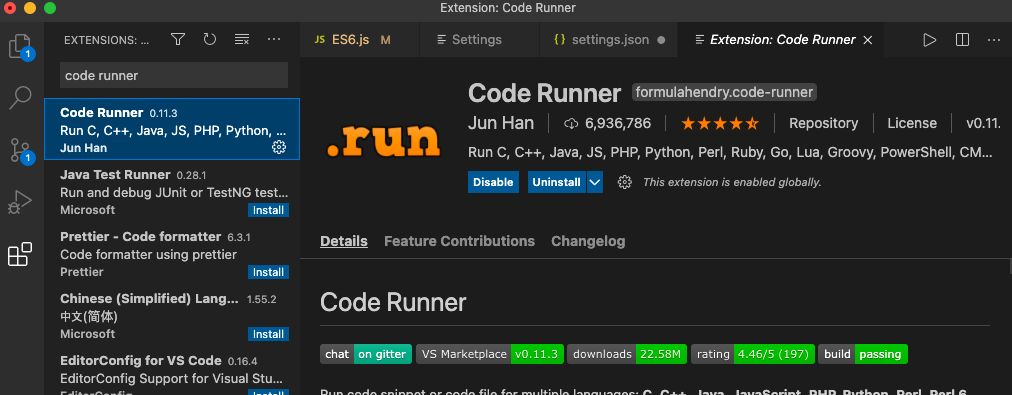
2. setting.json 수정
Code > Preferences > Settings
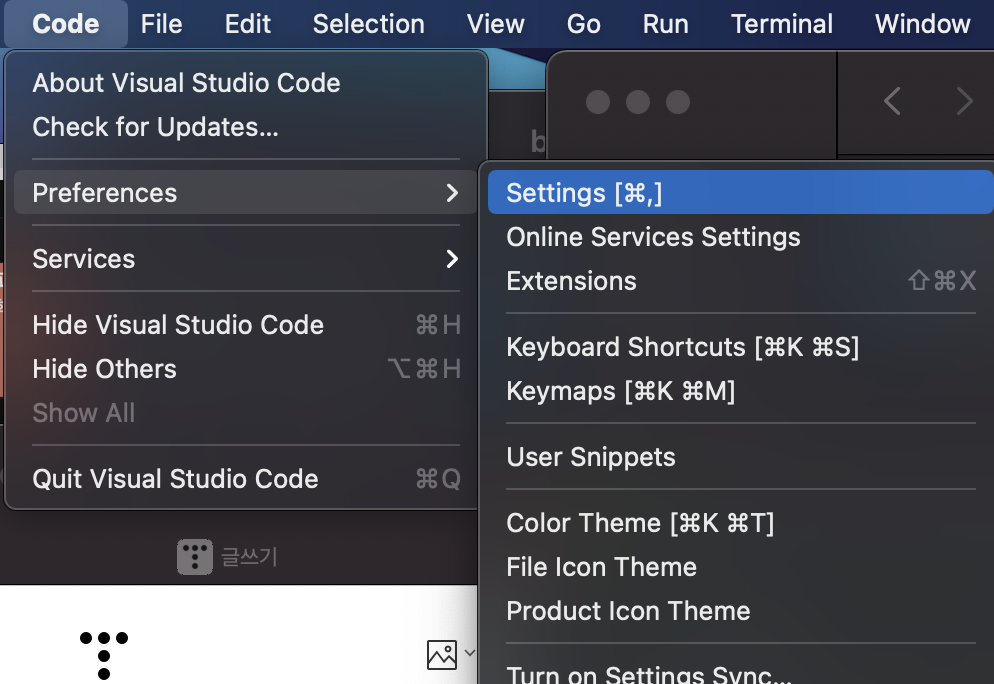
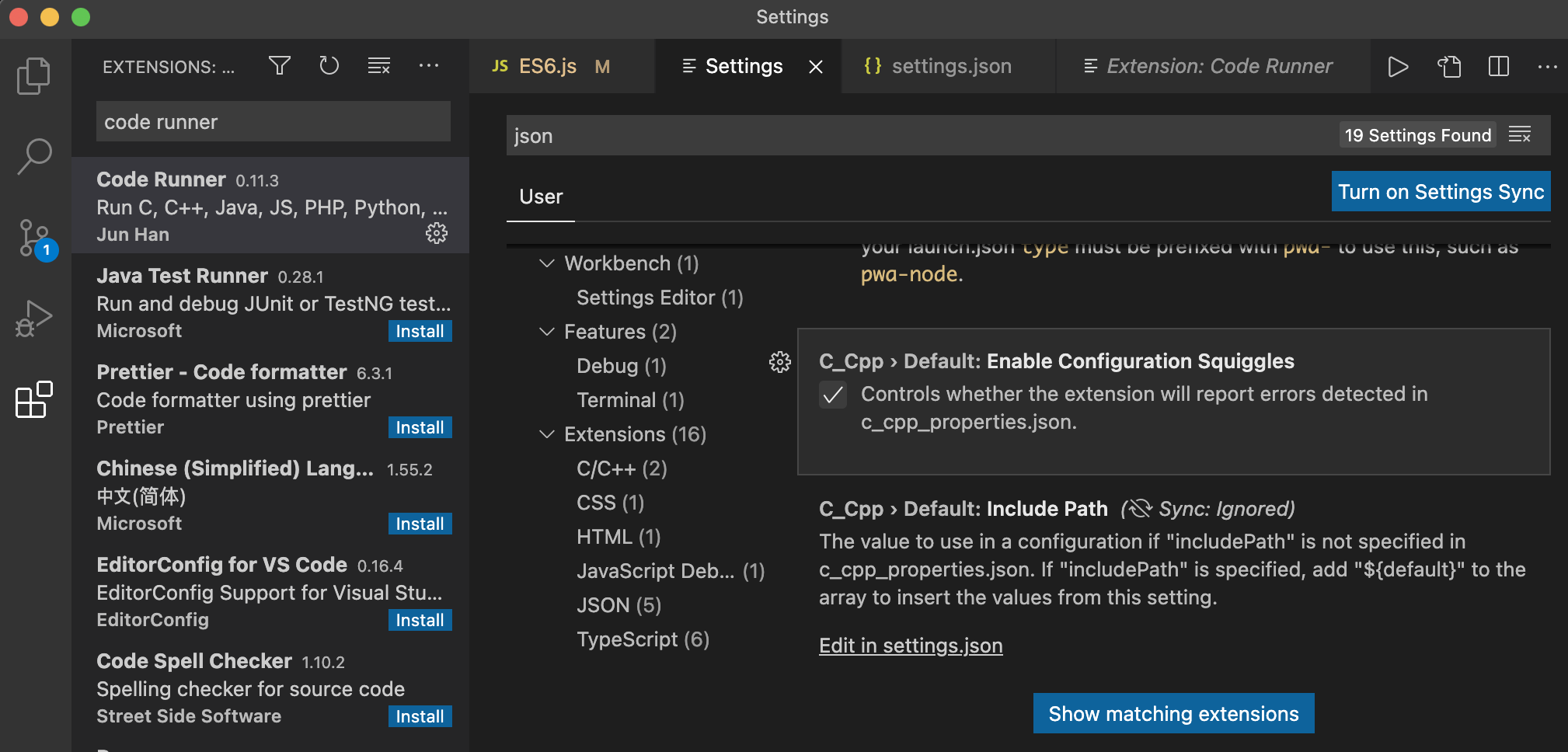
json을 검색하면 Edit in settings.json 이라는 것이 보인다 클릭하면 setting.json으로 들어갈 수 있음
{
"[json]": {
"editor.quickSuggestions": {
"strings": true
},
"editor.suggest.insertMode": "replace",
}
}
이렇게 기본으로 되어있던 setting.json 파일을
{
"[json]": {
"editor.quickSuggestions": {
"strings": true
},
"editor.suggest.insertMode": "replace",
},
"code-runner.runInTerminal": true,
}
다음과 같이 수정하면 Terminal로 ouput을 확인할 수 있다.
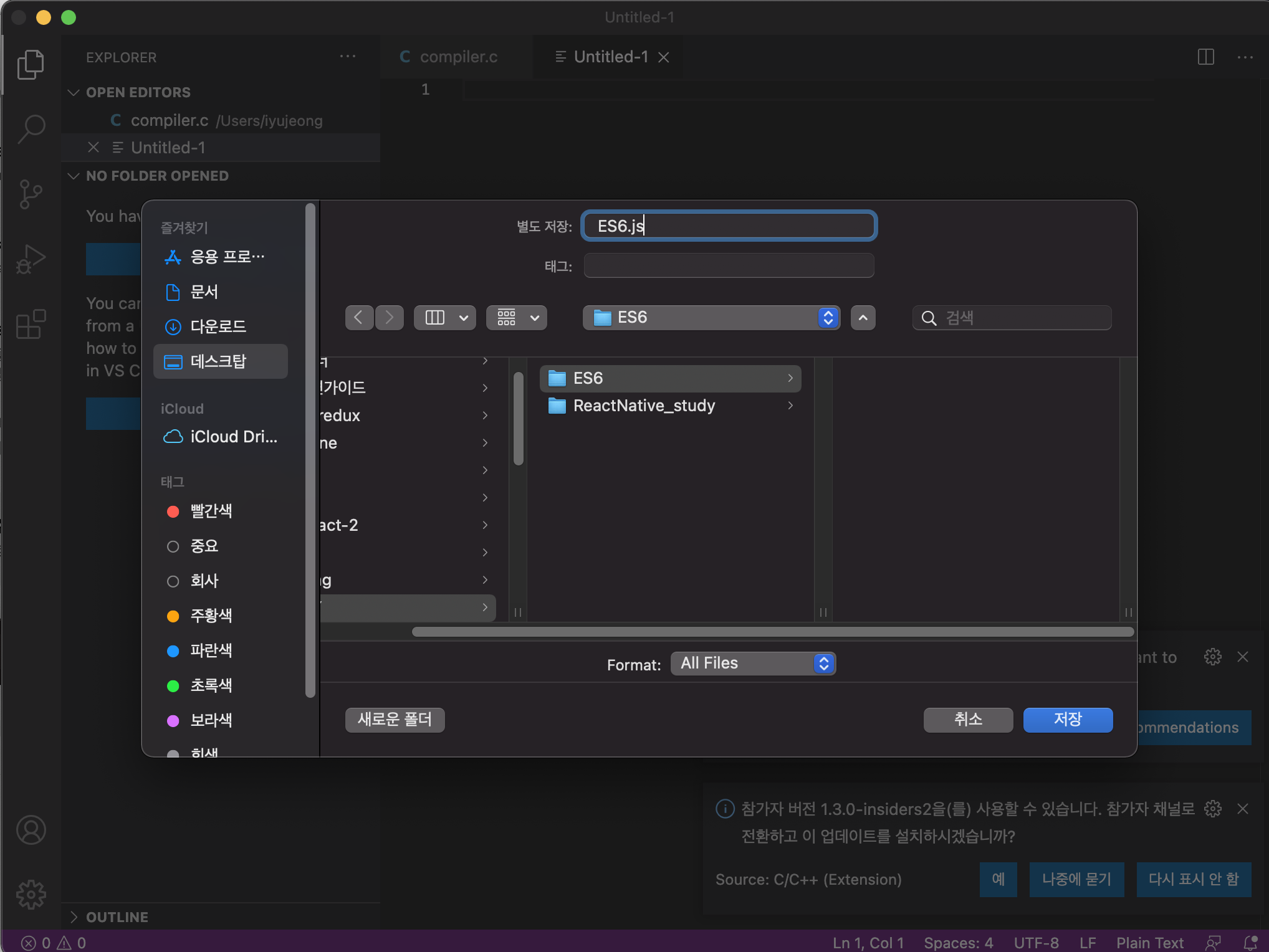
연습 파일 생성
원하는 폴더에 파일을 생성해주고 이름을 ES6.js로 생성해준다.
ES6필수 문법
변수
여러가지 타입을 가진 c언어 등과 다르게 javascript에서는 매우 유연한 변수를 가진다.
변수에는 var / let / const 로 3가지가 존재한다.
ES5에서는 var만 존재했는데, 여러가지 문제점이 있어 let / const가 추가되었다고 한다.
var
var가 가지는 문제점
1. function 단위의 scope을 가진다.
var는 block({ ... })단위가 아닌 function ( function() { ... } )단위의 scope을 가진다.
var hello = "world"; //전역변수
function test(){
var hello = 'korea' //지역변수
console.log(hello);
}
test(); // 지역변수 korea
console.log(hello); //전역변수 world
결과)
korea
world
이렇게 함수로 작성할 경우 함수 내 scope({ ... })에서는 지역변수 처럼 작용되지만,
함수가 아닌 block, 예를 들어 if문 같은 경우
var hello = "world"; //global variable
if(true){
var hello = 'korea' // local variable
console.log(hello); //korea
}
console.log(hello); //korea
결과)
korea
korea
두 경우 모두 전역변수/ 지역변수 이지만, 그 개념이 fuction단위에서만 적용되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
2. 같은 이름의 변수를 두번 선언 가능
일반적인 프로그래밍에서는 같은 이름을 가진 변수를 선언할 수 없다. (지역/전역 변수 처럼 범위가 다르지 않은 경우)
하지만, var에는 이 개념이 적용되지 않는다.
var hello = "world";
var hello = "korea";
console.log(hello);
결과)
korea오류 없이 출력됨
→ 해결 방법 : "let" 을 사용
let
let 을 사용하는 경우 위의 2가지 문제가 모두 발생하지 않음
fucntion이 아닌 block단위의 scope를 가지며,
let hello = "world"; //global variable
if(true){
let hello = 'korea' // local variable
console.log(hello); //korea
}
console.log(hello); //world
결과)
korea
world
같은 이름의 변수를 두번 선언할 수 없다 ( 에러를 발생 시킴 )
var hello = "world";
var hello = "korea";
console.log(hello);
결과) 에러메세지 출력
SyntaxError: Identifier 'hello' has already been declared
at wrapSafe (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1024:16)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1072:27)
at Object.Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1137:10)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:973:32)
at Function.Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:813:14)
at Function.executeUserEntryPoint [as runMain] (node:internal/modules/run_main:76:12)
at node:internal/main/run_main_module:17:47
const
상수로 변하지 않는 값을 의미한다.
변수를 재정의 할 시 오류가 발생한다.
const num = 5;
num = 6; //재정의
console.log(num);
결과)
/Users/iyujeong/Desktop/STUDY/ReactNative_study/ES6/ES6.js:18
num = 6;
^
TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.
at Object.<anonymous> (/Users/iyujeong/Desktop/STUDY/ReactNative_study/ES6/ES6.js:18:5)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1108:14)
at Object.Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1137:10)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:973:32)
at Function.Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:813:14)
at Function.executeUserEntryPoint [as runMain] (node:internal/modules/run_main:76:12)
at node:internal/main/run_main_module:17:47
참고) 지역변수, 전역변수는 같은 이름의 다른변수 취급이 가능하므로
const hello = "world";
if(true){
const hello = 'korea'
console.log(hello); //korea
}
console.log(hello); //world
BUT, 객체(object)나 배열(array)의 요소의 수정은 가능하다.
OBJECT
const drinks = {};
drinks.caffe = 'latte';
drinks.lemon = 'ade';
console.log(drinks)
drinks.caffe = 'americano';
drinks.lemon = 'tea';
console.log(drinks)결과)
{ caffe: 'latte', lemon: 'ade' }
{ caffe: 'americano', lemon: 'tea' }
ARRAY
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
arr[0] = 100;
arr[4] = 500;
console.log(arr);결과)
[ 100, 2, 3, 4, 500 ]
둘다 오류 없이 출력됨
String Literal
문자열과 변수들을 쉽게 다룰 수 있는 문법
""을 사용하던 기존 string과 다르게 ``와 $를 이용해서 표현한다.
`${variable_name}`
기존 String 표현 방법과의 비교
const val01 = "Hello"
const val02 = "World"
const val03 = val01 + ' ' + val02 + '!!!!!';
console.log(val03); //Hello World!!!!!
const litVal = `${val01} ${val02}!!!!!`
console.log(litVal); //Hello World!!!!!왜 쉽게 다룰 수 있는 문법인지 한눈에 알 수 있음
for ... of 반복문
객체(object)의 value값에 접근하는 방법을 제공함.
for ... in 반복문 : 객체(object)의 key값에만 접근이 가능 , value에는 접근이 불가능
let array = [10,20,30,40];
for (let val in array){
console.log(val); // 0 1 2 3
}
for (let val in array){
console.log(array[val]); // 10 20 30 40
}
for (let val of array){
console.log(val); // 10 20 30 40
}
symbol iterator 속성을 가지는 collection에서만 사용 가능
(== value값을 생성하면 key값이 저절로 생성되는 배열같은 객체에서만 사용 가능 )
let obj = {
a:1,
b:2,
c:3
}
for (let val of obj){
console.log(val); //error
}
for (let val in obj){
console.log(val); //a b c
}
for (let val in obj){
console.log(obj[val]); //1 2 3
}다음과 같이 key를 직접 지정한 경우 for .. of 사용 불가능 , in만 사용 가능
Rest Operator (... a)
모든 남은 인자(매개변수)들을 표준 자바 스크립트 "배열"로 대체하기 위한 문법
함수 정의시 인자 부분에 사용함
function printNums(num1, ...num2){
console.log(num1, num2);
}
printNums(1,2,3,4,5);
결과)
1 [ 2, 3, 4, 5 ]num1에 1인자로 배치한 뒤
... (rest operator)가 존재하므로 남은 2,3,4,5를 배열로 대체하여 num2 인자로 사용한다.
+추가) arguments
함수로 전달된 모든 인수를 포함하는 객체
function printNums(num1, ...num2){
console.log(arguments);
}
printNums(1,2,3,4,5);결과) 인자로 전달된 key/ value모두 출력됨
[Arguments] { '0': 1, '1': 2, '2': 3, '3': 4, '4': 5 }
Spread Operator
함수를 사용할 때 인수로 사용할 수도 있고, 배열/객체 안에 들어갈 수도 있음
함수를 호출할 때 사용함
함수에서 사용하는 경우
function sum (x,y,z){
return x+y+z;
}
//인자로 수를 부여할 때
console.log(sum(1,2,3)); // 6
// 인자로 배열을 사용할 때
let arr = [10,20,30];
//방법 1. 사용불가능
console.log(sum(arr)); // 오류
// 방법 2. apply함수 사용
console.log(sum.apply(null,arr)); // 60
// 방법 3. Spread Operator사용
console.log(sum(...arr)); // 60
응용)
function sum (a,b,c,d,e){
return a+b+c+d+e;
}
let arr = [20,30];
cosole.log(sum(10,...arr,40,50)); // 10 + 20 + 30 + 40 + 50 = 150
배열에 사용하는 경우
배열을 가지는 배열을 만들 때
let face = ['eyes', 'nose', 'mouth']
let head = ['hair', ...face, 'ears']
console.log(head) //[ 'hair', 'eyes', 'nose', 'mouth', 'ears' ]
배열을 복사할 때
let arr = [1,2,3];
let arrCpy = [...arr];
console.log(arrCpy); // [1,2,3]*주의)
let arrCpy = arr;이렇게 배열을 복사할 경우, arrCpy가 달라짐에 따라 arr도 똑같이 바뀜
객체에서 사용되는 경우
객체를 가지는 객체를 만들 때
let drinks = {
caffe: 'latte',
coca: 'cola'
}
let newDrinks = {
lemon: 'tea',
orange: 'juice',
...drinks
}
console.log(newDrinks);
결과)
{ lemon: 'tea', orange: 'juice', caffe: 'latte', coca: 'cola' }만약 Spread Operator(...)을 사용하지않고 그대로 drinks로 넣는 경우
객체 안에 객체가 들어가게됨
{
lemon: 'tea',
orange: 'juice',
{caffe: 'latte', coca: 'cola'}
}
Arrow Function
화살표(=>)를 쓰는 축약형 함수
표현식의 결과값을 반환하는 표현식 본문
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
let twice = arr.map(v=>v*2);
console.log(twice); // [2,4,6,8,10]
let twice = arr.map (function(val){
return val*2;
})
console.log(twice); // [2,4,6,8,10]표현식의 결과값을 return
arrow fuction이 훨씬 간결한 것을 알 수 있음
참고) map함수
for문과 같은 loop
js제공 배열 객체 내장함수 (배열을 대상으로 사용가능 → output이 배열 )
input으로 함수를 입력받아 output으로 배열을 return
함수의 두번째 인자는 배열의 인덱스값임
ex ) arr.map(a,b)
a는 배열의 value, b는 배열의 index
let arr = [10,20,30,40,50];
let twice = arr.map((v,i)=>{
console.log(`i: ${i}, v: ${v}`)
});
console.log(twice);결과)
i: 0, v: 10
i: 1, v: 20
i: 2, v: 30
i: 3, v: 40
i: 4, v: 50
상태 블록 본문에 쓰이는 경우
상태를 결정지음
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let twice = arr.map(v=>{
if(v%2 === 0) console.log('even number');
else console.log('odd number');
});결과)
odd number
even number
odd number
even number
odd number
Class
js에서 클래스는 함수처럼 사용됨
( java개념과 매우 유사)
//설계도
class Person{
//설계도에 들어갈 요소들
constructor(region_, gender_){
this.region = region_;
this.gender = gender_;
}
greetings(val = 'an-nyoeng'){
console.log(val);
}
}
//클래스 생성 -> 설계도 요소들을 입력해서 초기화
let korean = new Person('Korea','male');
console.log(korean); //Person { region: 'Korea', gender: 'male' }
//초기화된 값 변경 가능
korean.gender = 'female';
console.log(korean); //Person { region: 'Korea', gender: 'female' }
//상속
class American extends Person{
constructor(region_,gender_,language_){
super(region_,gender_); //부모클래스 생성자 rule을 따름
this.language == language_
}
//오버라이딩 : 부모와 자식간의 동일한 메소드가 있으면, 부모 메서드는 호출되지 않음
greetings(val = 'hello'){
console.log(val);
}
}
let american = new American('USA','female','English')
console.log(american); // American { region: 'USA', gender: 'female' }
american.greetings(); // hello
'Frontend > React-Native' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React-Native] View, Text, Style (0) | 2021.05.29 |
|---|---|
| [React] React기초(props / state) (0) | 2021.05.29 |
| [ReactNative] 프로젝트 시작및 시뮬레이터 (0) | 2021.03.29 |
| 리액트 네이티브(ReactNative)란? (2) | 2021.03.29 |
| [Silicon Mac M1] 안드로이드 에뮬레이터(Android Emulator)설치 (0) | 2021.02.08 |



